Breaking the Silence
Early support, Lifelong Confidence- Empowering Children to Communicate with Clarity
Therapies

When Words Are Delayed: Identifying, Understanding, and Treating Speech Delays in Children
Speech delay is a common developmental concern that can affect a child's ability to communicate effectively. While every child develops at their own pace, delayed speech can impact social skills, emotional regulation, and academic success. Understanding the causes, recognizing early signs, and implementing targeted interventions can help children overcome speech challenges and build strong communication skills.
Understanding Speech Delay and Its Causes
Speech delay occurs when a child does not reach expected speech milestones within the typical timeframe. Unlike language delay, which affects understanding and use of words, speech delay specifically refers to the difficulty in producing sounds and words clearly.
Common causes include
- Hearing Loss: Even mild hearing impairment can hinder speech development.
- Oral-Motor and Sensory challenges: Weak muscle coordination or sensory aversions can affect sound production.
- Neurodevelopmental Conditions: Autism, developmental delays, and other conditions can contribute to speech difficulties.
- Environmental Factors: Limited language exposure or excessive screen time may impact communication skills..
- Childhood Apraxia of Speech(CAS): A motor speech disorder that makes it difficult to plan and produce sounds correctly.
Recognzing the Signs of Speech Delay
Children develop speech at different rates, but key milestones can help identify potential delays:
- By 12 months: Lack of babbling, gestures, or response to their name
- By 18 months: Limited words, difficulty imitating sounds, or reliance on gestures instead of speech.
- By 2 Years: Fewer than 50 words, limited two-word combinations, or trouble following simple directions.
- By 3 Years: Unclear speech, difficulty forming sentences, or frustration when trying to communicate.
Effective Intervention Strategies
Early intervention is essential for improving speech outcomes. A speech-language pathologist (SLP) can assess the child's needs and recommend tailored therapy approaches, such as:
- Gestalt Language Processing: Unclear speech, difficulty forming sentences, or frustration when trying to communicate.
- Oral Placement Therapy (OPT): Strengthening oral muscles can improve articulation and sound production.
- Sensory-Based Speech Therapy: Multi-sensory techniques can support children with sensory processing differences.
- Auditory Verbal Therapy (AVT): Enhances listening and spoken language skills in children with hearing loss.
- Play Based and Interactive Strategies: Encouraging back-and-forth communication through play and daily interactions fosters speech development.
The Importance of early Intervention
Speech delay can have long-term effects on a child s communication, social skills, and academic performance if left unaddressed. Seeking professional guidance early can make a significant difference in a child's ability to express themselves confidently and meaningfully.
By understanding the causes, recognizing the signs, and implementing effective strategies, parents and professionals can support children in overcoming speech delays and unlocking their full communication potential.

Check Out More Articles
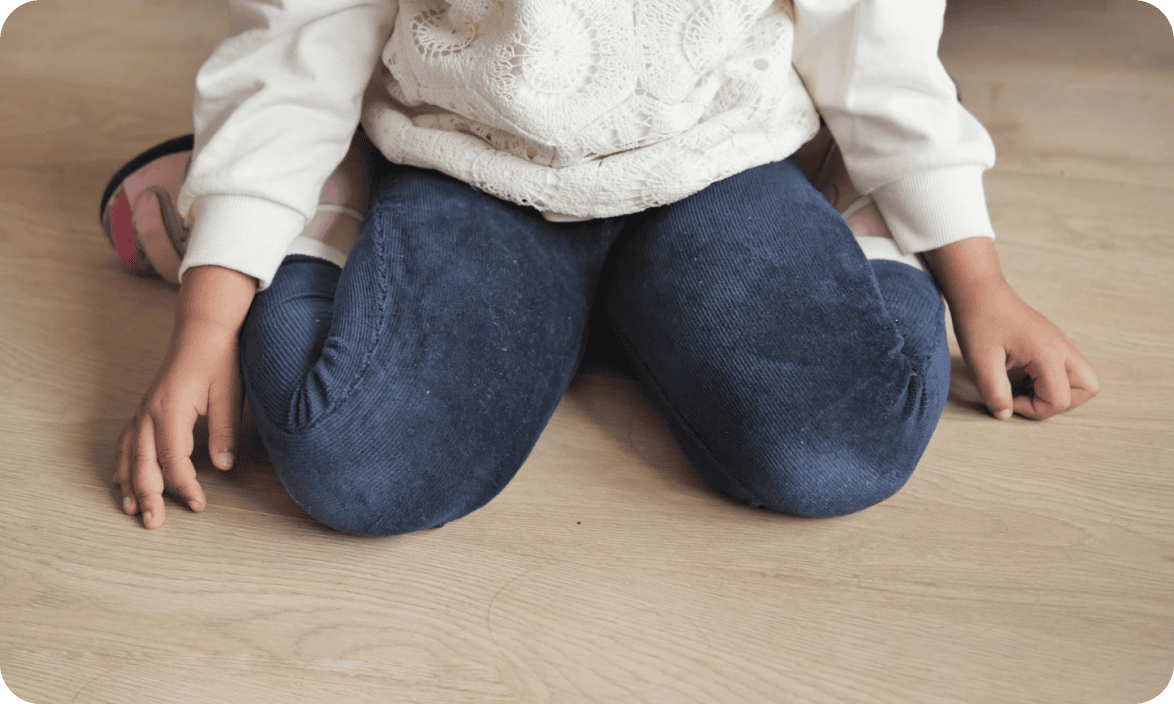

Child Development
W-Sitting: What you Need to Know
Better Posture, Stronger Movement- Help Your Child Sit right !

Therapies
Personalized ABA Therapy
Building Skills, reducing Challenges, and fostering growth.
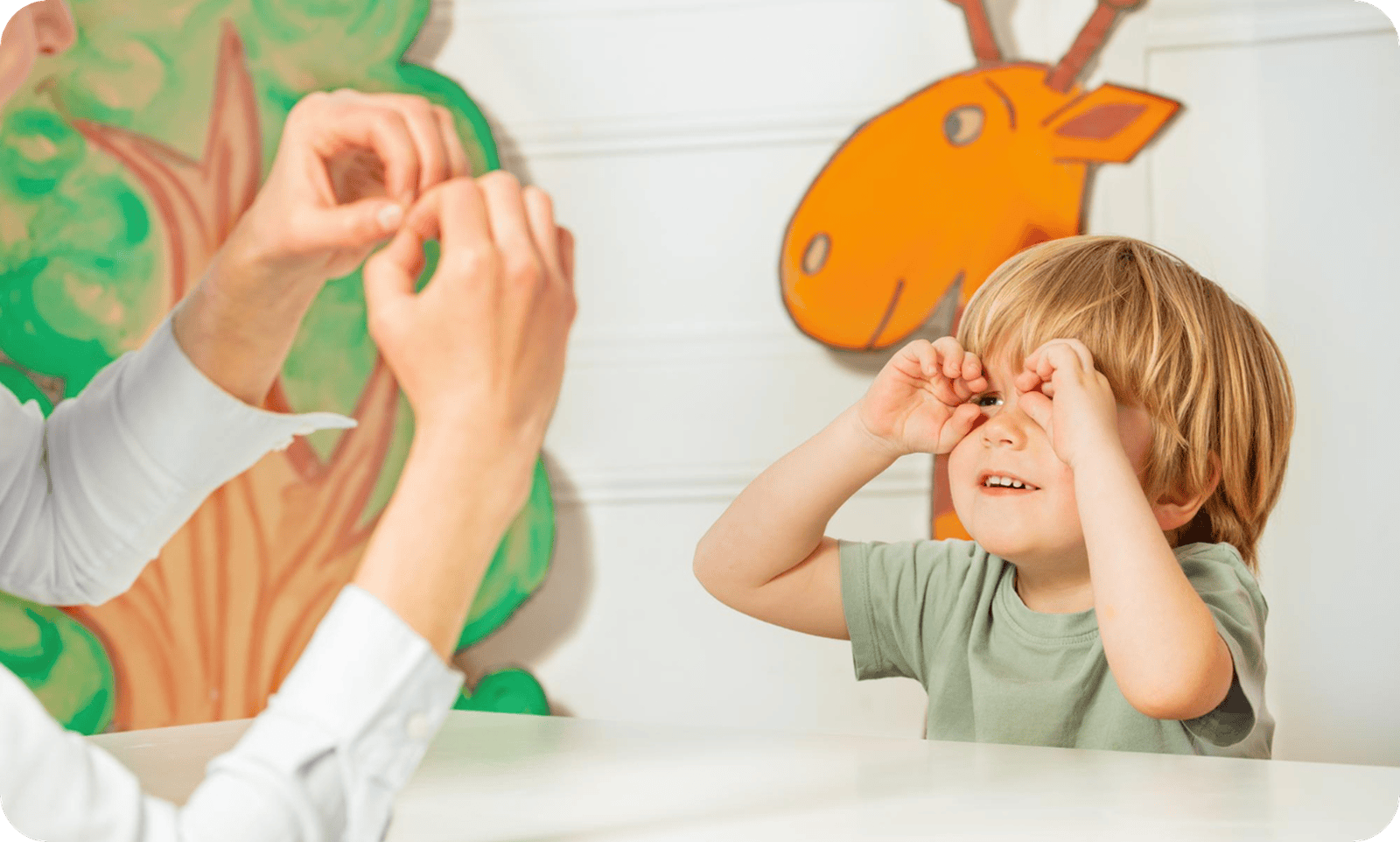

Occupational Therapy